Operator Fleet Procurement Considerations
With the expected launch of eVTOL services at the Paris Olympics in 2024 and the Osaka World Expo in 2025, aspiring eVTOL operators seeking to be early adopters need to develop their business plans and go-to-market strategies to support this vision. Vehicle selection is a key component of the equation, and there are four key fleet procurement considerations; we will be covering the first two considerations in this short post:
- Product Market Fit – Vehicle selection based on an operator’s unique use case and mission requirements
- Social Acceptance and Awareness – Public acceptance and its impact on operator business models
- Timeline on Certification / Entry into Service – OEMs’ ability to bring their vehicles into service (discussed in the next short post)
- Financing – Asset financing for operators (discussed in the next short post)
Product Market Fit
In our earlier post, we discussed the different use cases for eVTOLs. Several high-potential opportunities include passenger transportation, emergency response, freight, utility services (agricultural, industrial), and defense.
Exhibit 1. eVTOL Selected Use Cases
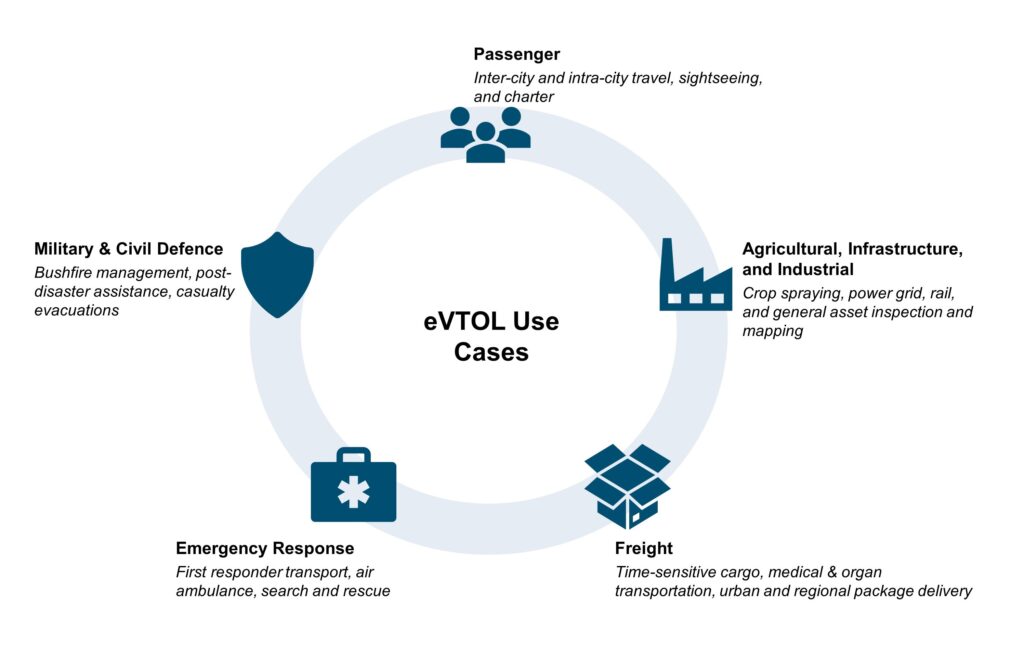
Source: Alton
However, as in the commercial or business aviation domain, there is no one-size-fits-all vehicle that addresses all the use cases. Range, payload, and infrastructure compatibility will impact eVTOL selection based on an operator’s business model.
- Range – Range directly influences the vehicle’s mission flexibility, market appeal, and its ability to serve urban and regional transportation needs.
- Payload – Payload capacity directly impacts the vehicle’s ability to carry passengers or cargo. Considering the currently limited power of eVTOL aircraft, operators need to find a balance between range and payload that aligns with their intended use case.
- Compatibility with Current Infrastructure – In order to ensure seamless operation of eVTOL aircraft, operators must ensure the availability of suitable landing sites, charging or refueling facilities, and air traffic management systems. Certain eVTOL models (e.g., those with hybrid-electric powertrains) may be better suited to leverage existing aviation infrastructure.
Operators must thus align their preferred aircraft specifications with their intended applications.
Notwithstanding the product market fit selection criteria, each vehicle will exhibit a different cost profile for a given mission. A detailed direct operating cost model against a representative network is critical in defining the right vehicle for the mission.
Social Acceptance and Awareness
Public perception, attitudes, and opinions will significantly influence the adoption and integration of eVTOLs into the social fabric of communities.
Social acceptance stems from three aspects: market acceptance, community acceptance, and political acceptance.
Market Acceptance
Securing confidence from consumers, financiers, and stakeholders is vital for ensuring the transformative progress of eVTOL technology within the aviation landscape. The shared belief and cooperation of these three key elements are crucial for successful commercialization.
- Consumers – It is imperative that eVTOL aircraft offer compelling use cases and distinctive value propositions that significantly enhance daily activities, in ways that existing transportation options cannot or do not provide.
- Financiers – The development of eVTOL technology requires significant capital investment. Investors, in turn, require a clear understanding of the potential returns associated with their investment. Although these returns may not materialize in the immediate future, OEMs must ensure that capital providers are confident in the OEM’s strategic pathway toward successful commercialization.
- Industry Players – Similar to traditional aviation, the design, manufacturing and operations of eVTOL aircraft necessitate extensive collaboration among a diverse array of industry stakeholders, including suppliers, aftermarket providers, infrastructure providers, transport planners, and regulators, among others. Without the collective belief and cooperation of the entire ecosystem, individual entities within the space will encounter challenges in making significant progress.
Community Acceptance
Community acceptance holds greater significance to residents and local authorities, as eVTOLs will operate in close proximity to or within communities. This is unlike airports, which are typically situated further away from densely populated urban cores. The impact is thus much more voluminous on local residents, and impact how authorities perceive, and regulate, the sector.
- Residents – The relationship between aviation operations and residential communities has traditionally been challenging, for various reasons such as visual and noise pollution, and safety issues. Overcoming the entrenched mindsets that communities may harbor about aviation and educating people about its benefits will help to address issues around the “Not-In-My-Back-Yard”(“NIMBY”) mentality that may arise in the early stages of eVTOL commercialization, and crucially, obtain buy-in from a key stakeholder group.
- Local Authorities – Authorities must contend with a variety of considerations regarding eVTOL development, such as transportation infrastructure planning that accounts for access and social equity issues, all of which needs to be organized and studied in detail.
It is thus critical to inform the local authorities of eVTOL’s value proposition, requirements, and its positive potential impact on communities. Developers will also need to educate authorities on the required resources and actions required for preparing to integrate this new technology.
Political Acceptance
Regulators and government policy makers all play important roles in ensuring the safe operation of eVTOLs and their acceptance by the wider public.
- Regulators – Civil Aviation Authorities (e.g. FAA, EASA) are mandated to ensure that the vehicles are on par with standards and are safe to operate. They will need to collaborate closely with OEMs and the Civil Aviation Authorities of other nations in order to design certification rules and processes for eVTOL design and manufacturing.
- Policymakers – In addition to regulatory bodies that assess the technical details of these aircraft, government policy makers can also help expedite the commercialization process by offering supportive policies / subsidies to improve the economic viability of the services provided. Their acceptance of eVTOLs will help facilitate the creation of an ecosystem of eVTOL players and foster further public awareness and acceptance.
Conclusion
Operators must develop a keen understanding of the vehicle type required, their target use cases, and potential roadblocks and supporting factors for social acceptance in order to facilitate a successful market entry approach. A unique value proposition, bundled with a supportive social and political environment, will fuel the commercialization of eVTOL aircraft. These are two of several key areas that operators should consider when acquiring eVTOLs.